Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats
Latest Blog Posts
Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats
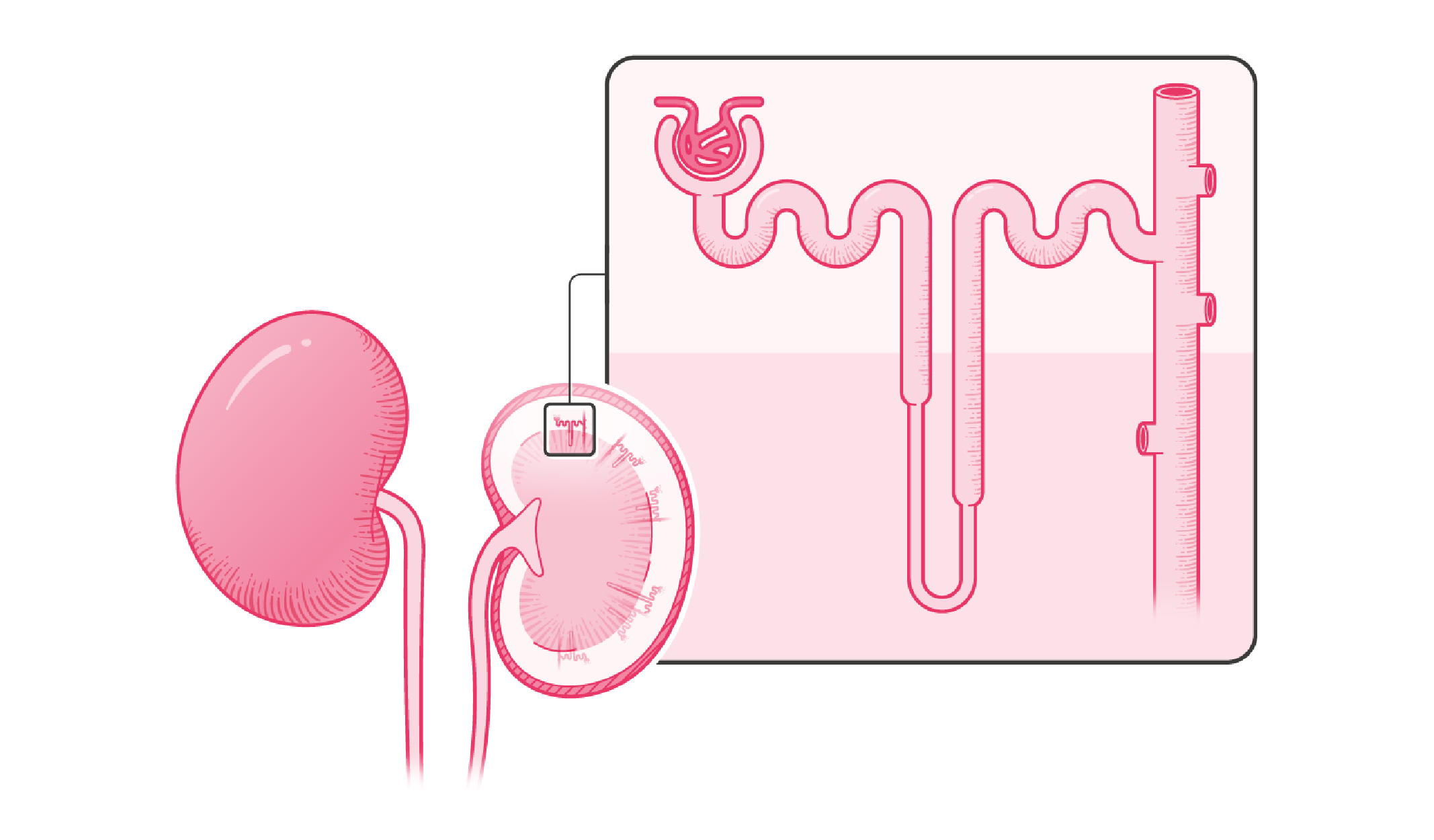
What are Nephrons?
Mammals have paired kidneys. In cats, each is composed of about 200,000 filtration units called Nephrons. Individual nephrons can be subdivided into four different regions…
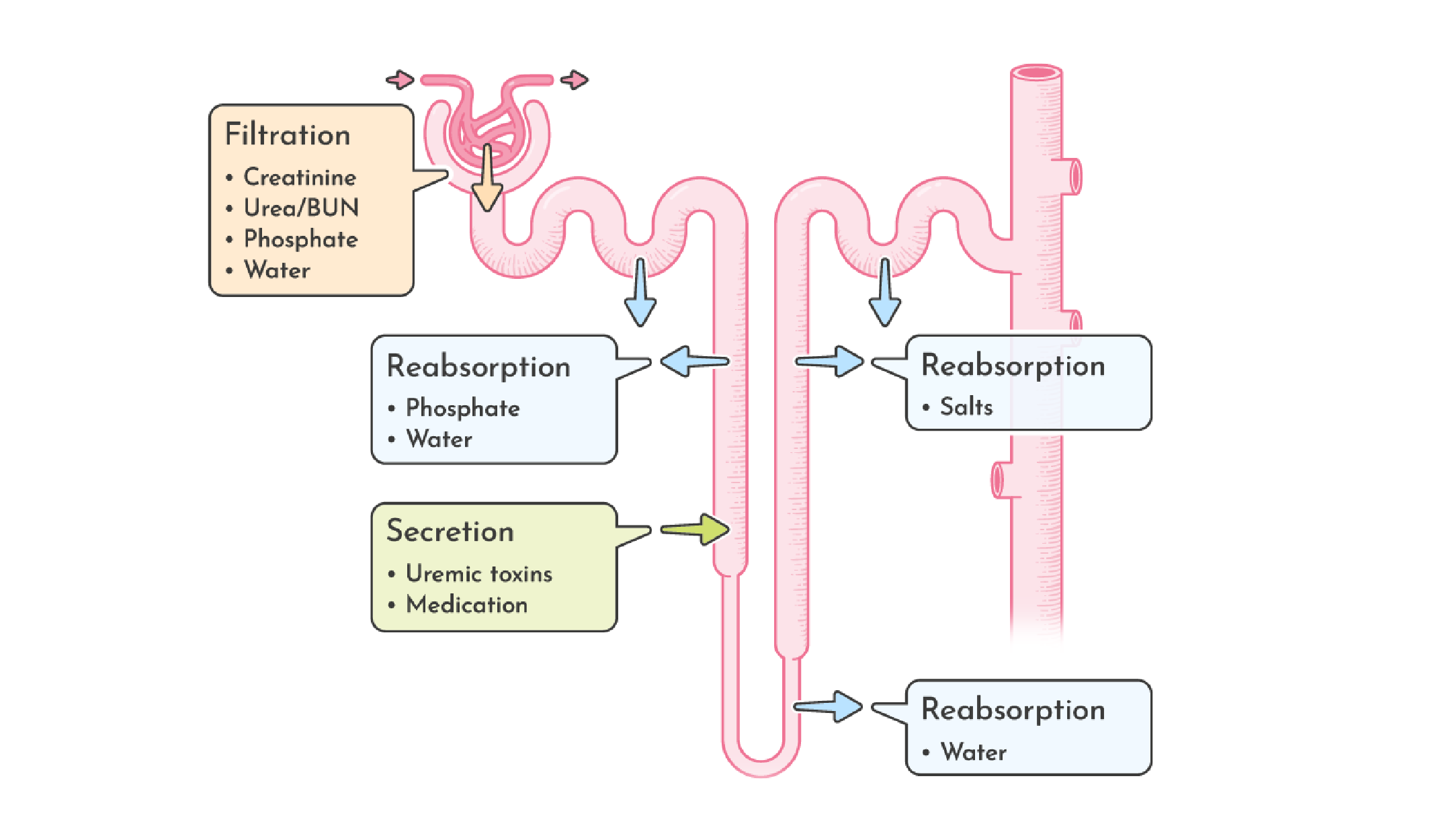
CKD and Kidney Function
The kidneys regulate water and electrolyte/mineral loss and thus balance the volume of water in the body. Excess electrolyte and excess water are eliminated.
Renal Failure
The consequences of renal insufficiency on renal function in the chronic kidney diseased cat.
Four vicious cycles
The progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is influenced by various mechanisms, all of which lead to further nephron loss. This loss…
Cats as Carnivores
It has been said that cats are just “little dogs”, but that’s not really the case. Cats, unlike dogs, are “obligatory carnivores” – their diet…
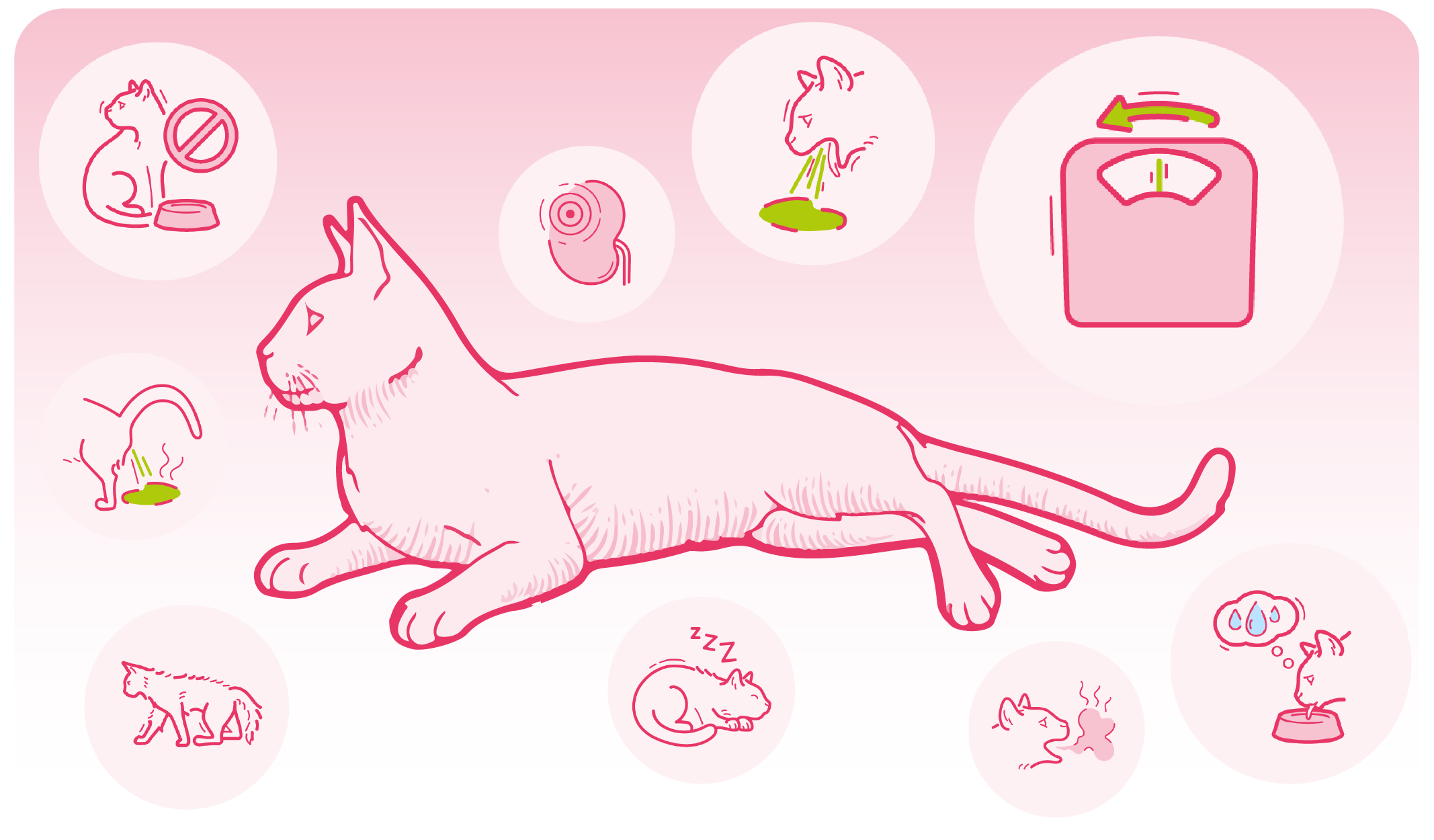
Clinical Symptoms
The clinical symptoms of CKD are as diverse and numerous as the functions of the kidney. In addition, each cat…
Diagnosis
Blood Tests
The usual tests to diagnose CKD measure the levels of creatinine and urea in the serum. In chronic kidney disease (CKD), both values are elevated. Diagnosis of CKD, however, requires more…
Urine Analyses
Urine analysis alone is highly indicative for kidney disease. Analysis reveals the presence of cells and bacteria in the urine, which indicate an inflammatory process. In addition, the pH of urine, urine specific gravity…
Further Blood Tests
Calcium is a mineral that plays an important role in muscle movements (muscle contraction), in blood clotting and also in nerve function. However, most calcium in the body is in the bones…
Radiological Tests
Healthy kidneys are unremarkable in X-ray scans. In general, X-ray scans of the kidneys can provide information about changes in size, growths…
Blood Pressure Measurement
Monitoring a CKD cat’s blood pressure is extremely useful. This is done with the help of special blood pressure cuffs…